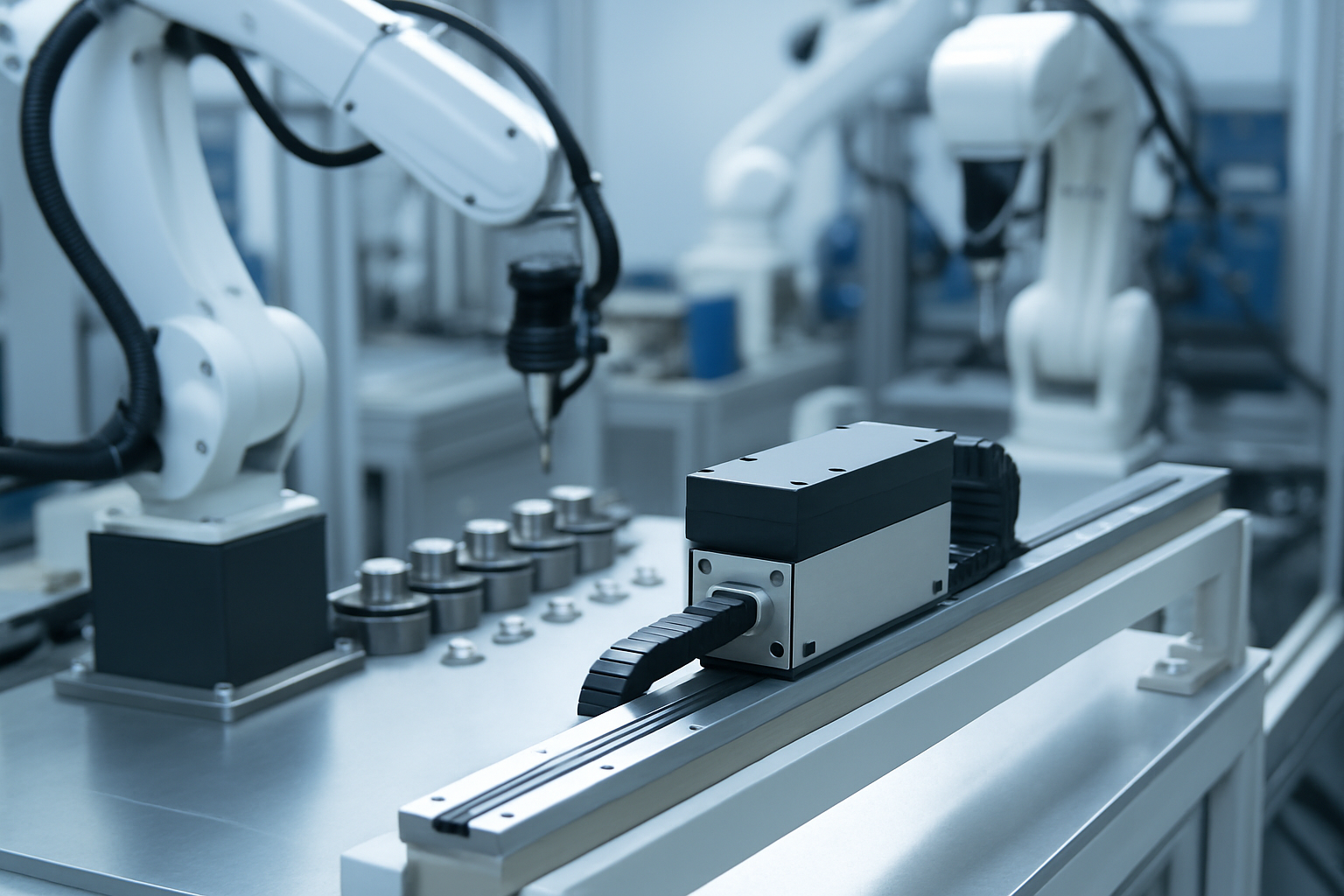
Linear motion lies at the core of many industrial and technological advancements, especially in fields where high-speed, high-precision movement is required. Linear motors are the perfect solution for such needs. This article will dive deep into what is the linear motion of a linear motor, covering principles, technologies, and applications behind these essential components.
Table of Contents
What Is the Linear Motion?
Linear motion refers to the movement of an object or system along a straight path. Unlike rotational motion, where movement occurs around an axis, linear motion involves displacement in a straight line. It is one of the fundamental forms of motion used in machinery, automation, and robotics. In the context of electric motors, linear motion is typically generated by converting the rotary motion of a traditional motor into straight-line movement through mechanical means. However, linear motors bypass this step entirely and generate straight-line motion directly.
How Does a Linear Motor Work?
A linear motor operates on the same principles as a conventional rotary motor, except it is essentially “unrolled.” Instead of producing torque to rotate a shaft, it generates force to move an object linearly along a track.
Components of a Linear Motor
Primary Part (Forcer): Contains coils and receives electrical input.
Secondary Part (Magnetic Track): Contains permanent magnets or conductive plates.
When current flows through the primary windings, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the magnets in the secondary, producing thrust and driving the mover along a linear path. This direct-drive mechanism eliminates backlash, mechanical wear, and vibration—resulting in exceptional accuracy and efficiency.
Types of Linear Motors
There are several types of linear motors, each suited for different applications:
Iron-Core Linear Motors
These motors have high force output and good thermal characteristics, making them suitable for heavy industrial applications. However, they may produce cogging forces.
Ironless Linear Motors (Coreless)
Designed for ultra-precise applications, these motors offer smooth, cog-free motion but with less force compared to iron-core types. They are ideal for semiconductor equipment and precision metrology.
Tubular Linear Motors
These offer a cylindrical form factor and are typically used in linear actuators for compact spaces. They can efficiently replace pneumatic or hydraulic systems.
Linear Stepper Motors
Operate in discrete steps, offering a cost-effective solution for applications requiring simple control and moderate precision.
Advantages of Linear Motors
Linear motors present numerous benefits that make them highly preferred in modern engineering:
Direct linear actuation: No gears, belts, or screws needed.
High acceleration and velocity: Enables faster cycle times.
Exceptional precision and repeatability: Perfect for micro-positioning tasks.
Minimal maintenance: Fewer moving parts mean less wear and tear.
Quiet and smooth operation: Ideal for environments requiring low noise and vibration.
Industrial Applications
Linear motors are used across various industries thanks to their performance characteristics.
Semiconductor Manufacturing
Wafer stages, lithography systems, and inspection tools use linear motors for nanometer-level positioning accuracy.
Robotics and Automation
In robotic systems, linear motors enable smooth and rapid movements, especially in pick-and-place and robotic arm applications.
CNC Machines
Precision cutting, milling, and engraving machines benefit from the speed and accuracy offered by linear motors.
Medical Equipment
Devices like MRI and CT scanners use linear motors for smooth patient table movements and scanning components.
Maglev Transportation
Linear induction motors are used in high-speed trains for frictionless, efficient movement.
Design Considerations
When integrating a linear motor into a system, several parameters must be evaluated:
Force and Speed Requirements: Choose the motor type and size accordingly.
Travel Length: Must match the application's linear displacement needs.
Cooling Needs: High-speed motors may require active cooling.
Feedback Devices: Encoders or linear scales may be required for position feedback.
Mounting Structure: Ensure the base is rigid and aligned properly.
The Future of Linear Motion with Linear Motors
Linear motor technology continues to evolve. With advancements in materials, controls, and feedback systems, they're poised to become even more integral to smart manufacturing and robotics.
Emerging Trends
Integration with AI and machine learning for predictive motion control
Vacuum-compatible linear motors for space and cleanroom environments
Increased adoption in medical robotics and microfluidics
Hybrid systems combining linear motors with piezo or voice coil actuators
FAQ
Q1.What is the linear motion of a linear motor?
It refers to the straight-line movement produced directly by the motor without converting rotary motion. This motion is achieved through electromagnetic interactions within the motor's structure.
Q2.What industries use linear motors the most?
Electronics, robotics, aerospace, automotive, medical, and transportation industries are key users.
Q3.Can linear motors replace all traditional rotary systems?
Not always. Rotary systems are still ideal for some long-distance or rotational tasks. However, linear motors excel where direct, high-speed, and precise linear movement is needed.
Q4.Are linear motors energy efficient?
Yes. They reduce mechanical losses and often provide better overall system efficiency due to direct-drive architecture.
Conclusion
Linear motors have transformed the way we think about motion in machines. Their ability to deliver high-performance linear motion without intermediate components makes them a game-changer across industries. By understanding how they work, the types available, and their advantages, engineers can make more informed decisions in designing cutting-edge systems.















 En
En


