Linear Motors: Becoming the Core Drive for High-End 3D Printing Equipment in the Pursuit of Higher Precision and Speed
In the 3D printing field where higher precision and speed are pursued, linear motors are rapidly emerging as the preferred drive core for high-end equipment.
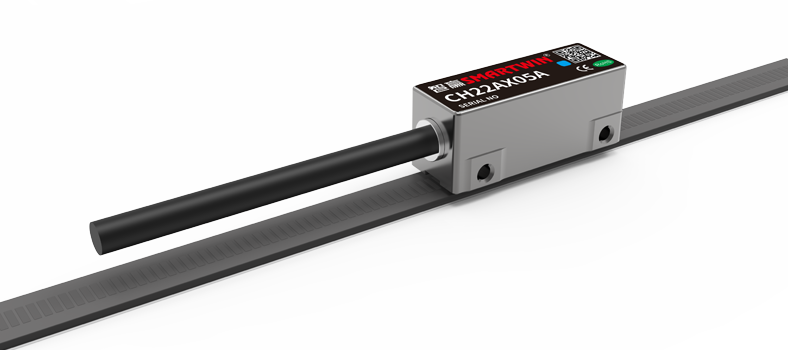
They break the reliance of traditional rotary motors on complex transmission chains such as lead screws, belts, or gears. Instead, they directly generate linear electromagnetic thrust between the mover (coil) and stator (magnetic rail), enabling precise driving of the printing platform or print head to achieve linear motion.
This "direct drive" mode brings revolutionary advantages to 3D printing technology:
Ultra-high Precision and Resolution: It eliminates errors such as mechanical backlash and elastic deformation, easily achieving micron-level or even higher positioning accuracy. This provides core technical support for printing complex and delicate structures.
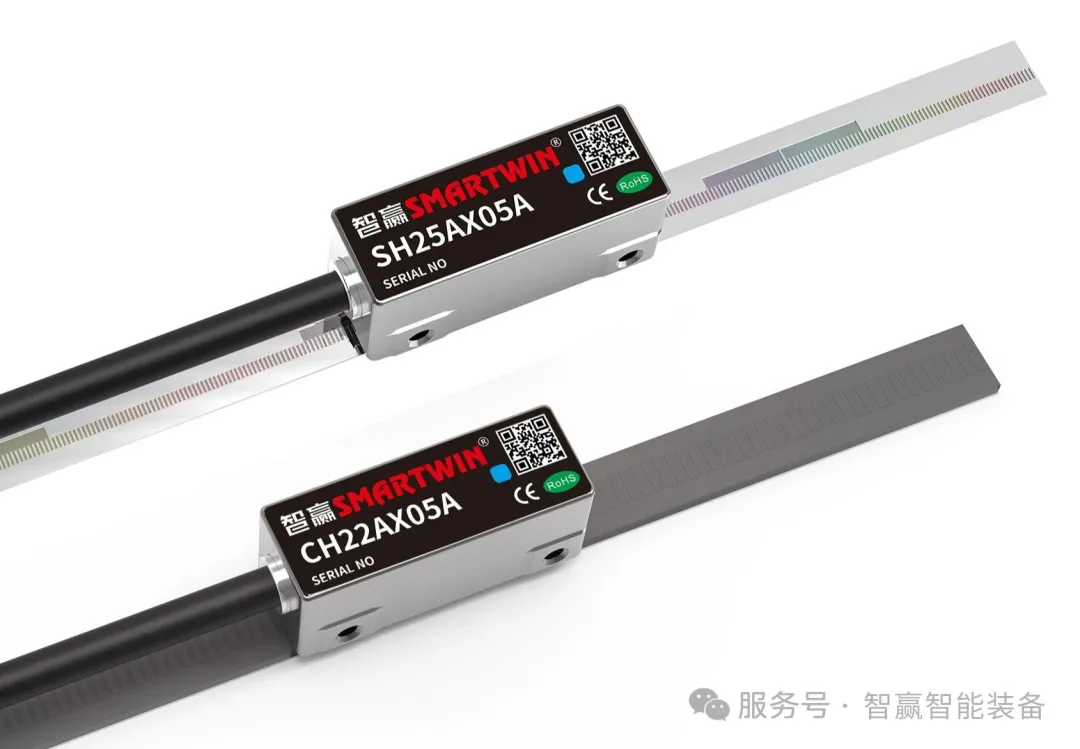

Rapid Response and High-Frequency Motion: The acceleration can reach several times that of traditional transmission methods, significantly improving the start-stop efficiency and scanning speed of the print head. This effectively shortens the overall printing cycle and enhances production efficiency.
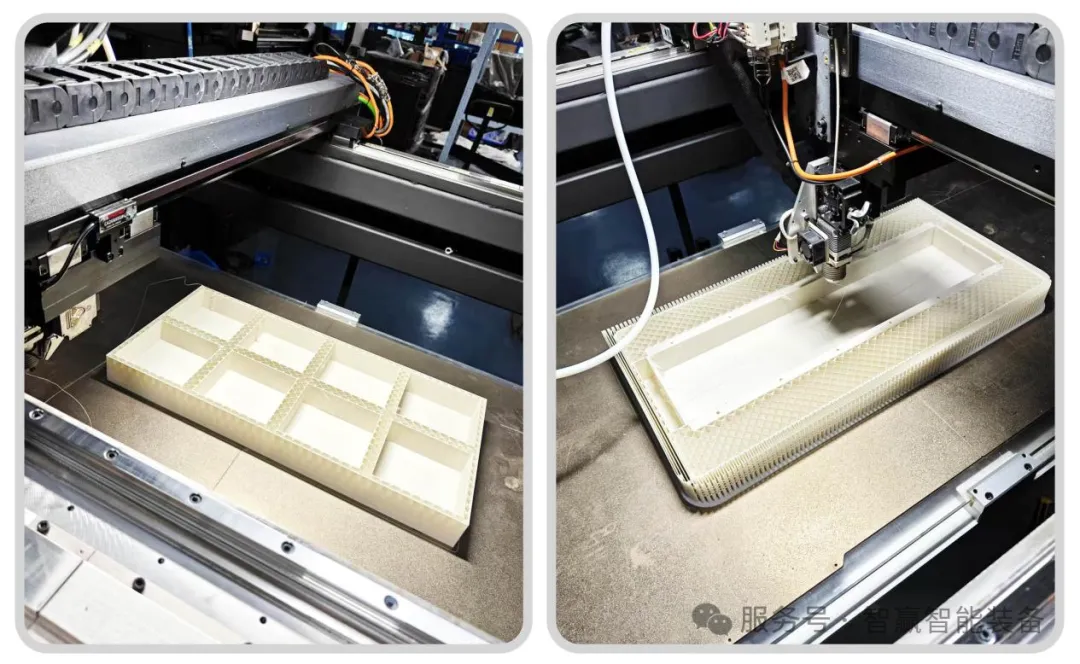
More Stable and Low-Noise Operation: Adopting a non-contact transmission design, it features minimal friction and weak vibration. This can effectively reduce resonance during the printing process, thereby improving the interlayer bonding quality and surface finish of printed parts.
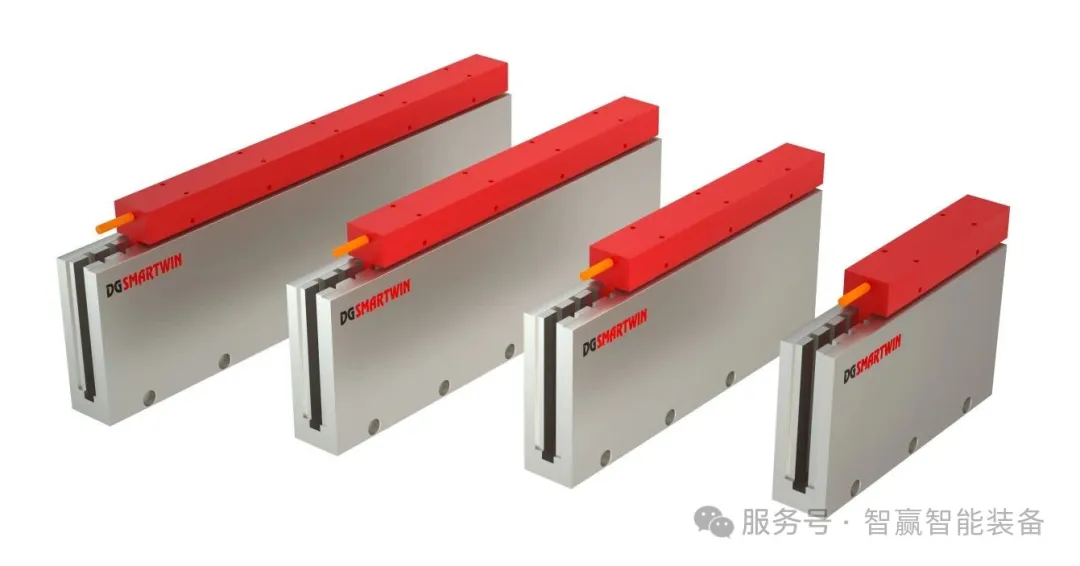

Simplified Structure and High Reliability: By eliminating intermediate transmission components, the equipment system becomes more compact. This not only reduces daily maintenance requirements but also further enhances the stability of the equipment during long-term operation.

In practical applications, the advantages of linear motors are particularly prominent. In industrial-grade 3D equipment, they can drive scrapers or laser galvanometers to achieve high-speed and precise powder spreading and scanning operations.
In high-end metal 3D printers, even in high-temperature working environments, linear motors can still ensure stable and accurate positioning of the hot bed or optical system. Additionally, in some 3D printing equipment that pursues extreme performance, linear motors are also used to drive nozzles or platforms to meet higher-standard printing requirements.
Although the cost of linear motors is higher than that of traditional transmission solutions, their outstanding dynamic performance and unparalleled positioning accuracy continue to drive industrial-grade and professional-grade 3D printing equipment to break through performance boundaries. From shortening production cycles to improving the quality of printed parts, linear motors have become a key engine for realizing high-efficiency and high-quality additive manufacturing. They can be truly regarded as the powerful "linear power" endowed by the era of precision manufacturing to 3D printing technology.















 En
En


