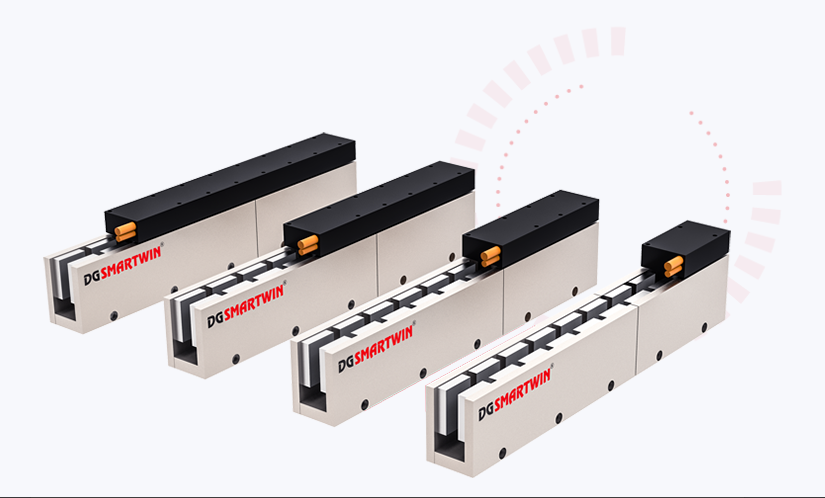
When it comes to precision motion control, choosing between iron core linear motors and ironless linear motors is a critical decision that can impact the performance and efficiency of your equipment. Both types of linear motors have unique advantages and applications, but understanding their differences is essential for making the right choice. In this article, we will explore the key distinctions, benefits, and applications of these two motor technologies, helping you determine which is best for your specific needs.
What Are Iron Core Linear Motors?
Iron core linear motors are a type of direct-drive linear motor that uses a laminated iron core for the stator. This core interacts with the magnets to generate the necessary electromagnetic force for motion. Iron core linear motors are known for their ability to produce high force density, making them ideal for applications where high power and torque are required.

Advantages of Iron Core Linear Motors:
1. High Force Output: The presence of the iron core allows for a greater electromagnetic interaction, which results in higher force production compared to ironless motors.
2. Cost-Effectiveness: Iron core linear motors are generally more affordable due to simpler construction and lower manufacturing costs.
3. Efficient Use of Space: These motors tend to have a compact design, offering higher force per unit volume, which is beneficial in applications with space constraints.
4. Heat Dissipation: The laminated iron core improves heat dissipation, making these motors more reliable in high-power applications.
Applications of Iron Core Linear Motors:
· CNC Machines: Their high force and torque make iron core linear motors ideal for CNC machines, especially in heavy-duty cutting or milling.
· Automation and Robotics: Industries requiring high precision and load-bearing capabilities benefit from the power density of iron core motors.
· Packaging Equipment: Their ability to handle fast, repetitive motion makes them ideal for industrial packaging systems.
What Are Ironless Linear Motors?
On the other hand, ironless linear motors, as the name suggests, do not have an iron core in their stator. This type of motor consists of a forcer (or coil assembly) and a magnet track, without any iron laminations. Ironless linear motors are known for their smooth motion and low cogging, which results in superior accuracy and precision.

Advantages of Ironless Linear Motors:
1. Zero Cogging: The lack of an iron core eliminates cogging, providing extremely smooth motion, which is critical for high-precision applications.
2. Higher Precision: Due to their design, ironless motors offer superior accuracy, making them ideal for applications that require fine positioning and control.
3. Low Weight: With no iron core, ironless linear motors are lighter, allowing for faster acceleration and better dynamic performance.
4. Minimal Heat Generation: These motors generate less heat, which is crucial for environments where temperature control is critical.
Applications of Ironless Linear Motors:
· Semiconductor Manufacturing: Precision is key in this industry, making ironless motors an ideal choice for wafer handling and other fine tasks.
· Medical Devices: Ironless linear motors are widely used in medical imaging and diagnostic equipment where precision and smooth motion are critical.
· Laboratory Automation: The smooth, precise motion of ironless motors is perfect for lab equipment such as liquid handling systems and automated testing machines.
Iron Core Linear Motors vs Ironless Linear Motors: Key Differences
1. Force Production
· Iron Core Linear Motors: Due to the iron in their stator, these motors generate higher force, making them more suitable for heavy-duty applications.
· Ironless Linear Motors: While they produce less force, ironless motors excel in applications requiring precision and low cogging.
2. Cogging and Precision
· Iron Core Linear Motors: These motors may experience cogging due to the interaction between the iron core and the magnets. While not ideal for high-precision tasks, they work well in applications where force outweighs the need for fine precision.
· Ironless Linear Motors: Without an iron core, cogging is virtually eliminated, providing smooth and precise motion control.
3. Weight and Acceleration
· Iron Core Linear Motors: The iron core adds weight, which can affect acceleration and dynamic response.
· Ironless Linear Motors: These motors are lightweight, allowing for faster acceleration and more efficient operation in high-speed applications.
4. Cost
· Iron Core Linear Motors: Generally more cost-effective due to simpler construction and widespread industrial use.
· Ironless Linear Motors: While offering superior precision, these motors are often more expensive due to the complexity of their design and manufacturing process.
Which Motor Is Right for You?
Choosing between iron core linear motors and ironless linear motors ultimately depends on your specific application requirements. If your project demands high force and torque in a compact space, iron core linear motors are likely the better choice. They provide excellent cost-effectiveness and power density, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial tasks.
However, if precision and smooth, cogging-free motion are critical, then ironless linear motors are the optimal choice. They excel in environments where accuracy and delicate handling are essential, such as in semiconductor manufacturing and medical applications.
Conclusion
Both iron core linear motors and ironless linear motors offer unique advantages, but understanding their differences will help you choose the right solution for your motion control needs. If you're looking for high-force, cost-effective motors, iron core linear motors are the way to go. But if you need precision and smooth performance, ironless linear motors provide the perfect solution.
Whichever motor you choose, it's essential to consider the specific demands of your application and the performance characteristics of each motor type to ensure optimal results.















 En
En


