Integrating a linear motor into a motion system isn't just about choosing the right motor—it requires coordinated integration with servo drives and encoders to unlock precision, stability, and full system performance. Whether you're building a pick-and-place machine, laser cutter, or semiconductor inspection stage, your motion control strategy hinges on seamless component compatibility.
In this guide, we walk through the best practices and essential considerations for integrating Smartwin's linear motors with servo drives and feedback encoders to create a robust, responsive motion system.
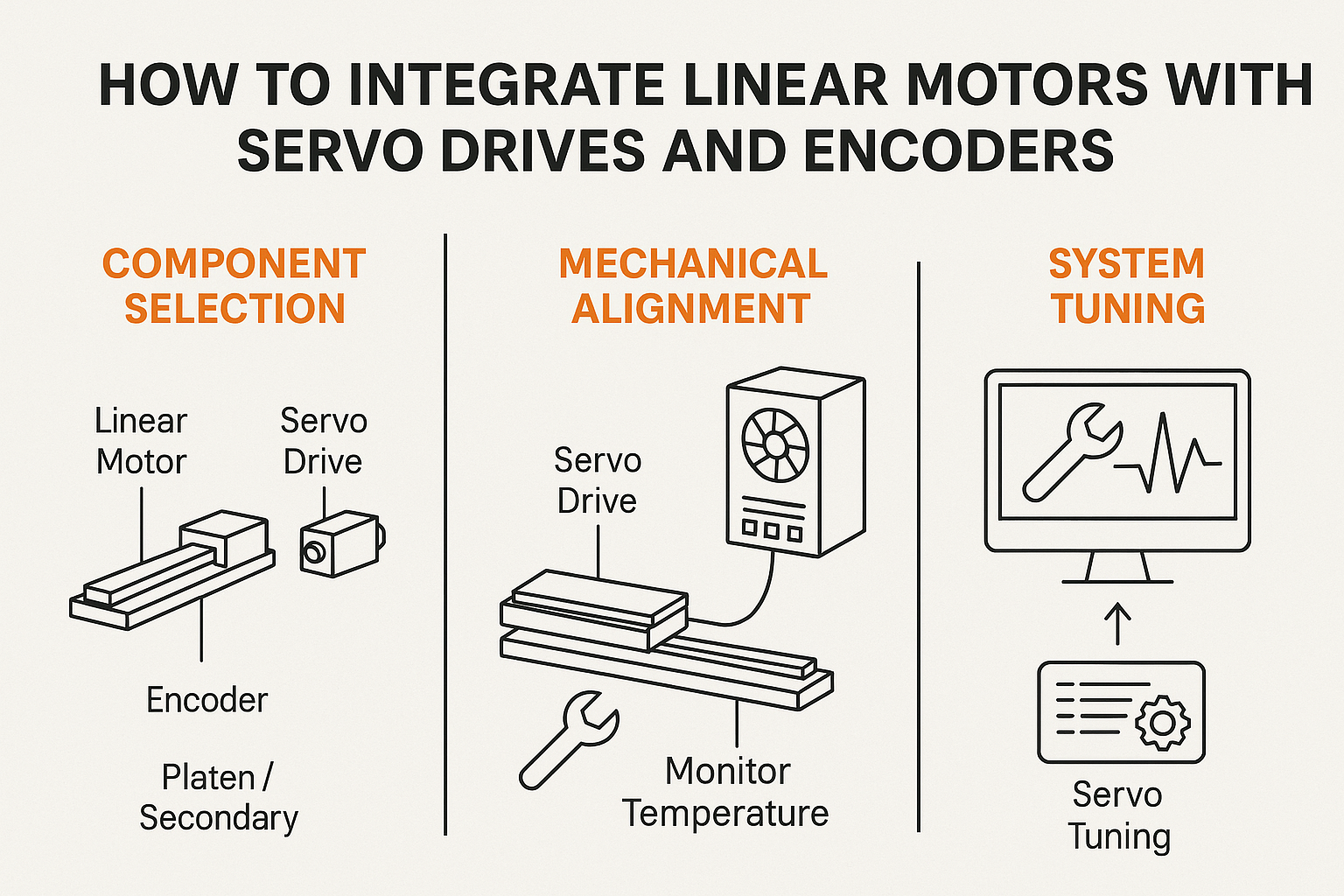
Understanding the Integration Triangle: Motor + Drive + Encoder
A linear motion system typically includes:
Linear Motor: Provides direct drive, high-speed linear movement (iron-core or ironless)
Servo Drive (Amplifier): Supplies current to the motor based on control signals
Encoder (Feedback Device): Measures position and velocity to close the feedback loop
These three components must be electrically and mechanically compatible, and properly configured in software.
Choosing the Right Linear Motor
Smartwin offers two main categories of linear motors:
Iron-Core Motors:
Higher thrust force
Best for heavy loads and industrial automation
Ironless Motors:
No cogging; smoother motion
Ideal for precision applications (semiconductor, optics)
Consider:
Stroke length
Required acceleration
Peak and continuous force
Mounting constraints
Selecting a Compatible Servo Drive
The servo drive (also called a motion amplifier) is responsible for powering the motor and executing control loops based on encoder feedback.
Key Parameters to Match:
Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensure the drive can handle the motor's continuous and peak current
Motor Type Support: Confirm the drive supports linear motors (not all rotary drives are compatible)
Feedback Interface: Drive must accept the encoder signal format (TTL, A/B/Z, SinCos, BiSS, etc.)
Recommended Drive Features:
Current and velocity loop tuning
Position control via external or internal controller
Safe torque off (STO) functionality
Smartwin motors are compatible with most mainstream industrial drives, including those from Delta, Yaskawa, Kollmorgen, and Beckhoff.
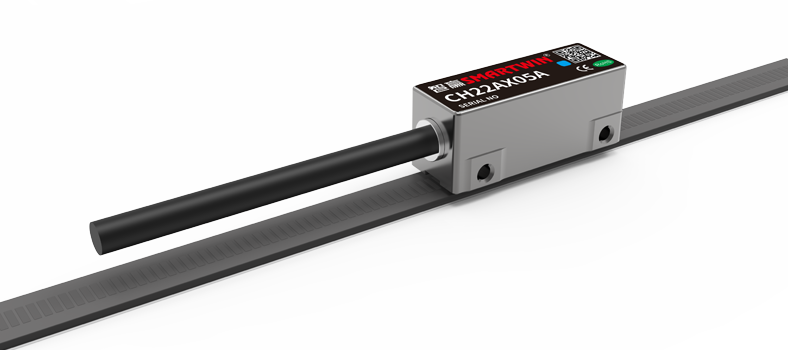
Encoder Selection and Mounting
Encoder Types:
Magnetic Encoders: Durable and compact; good for rugged environments
Optical Encoders: Higher resolution and accuracy; ideal for cleanrooms and metrology
Linear Gratings: Provide direct linear position sensing
Key Factors:
Resolution: Defines the smallest detectable position increment (e.g., 1 µm, 0.1 µm)
Interpolation: Some drives offer electronic interpolation for smoother feedback
Mounting Tolerance: Follow OEM specs for alignment and air gap
Best Practices:
Use shielded cables for encoder signals
Keep encoder cables separate from motor power lines
Verify signal compatibility between encoder and drive
Mechanical Integration and Alignment
Mounting:
Ensure the motor and encoder are mounted to a flat, rigid surface
Use alignment dowels or precision tooling holes if available
Maintain the specified air gap between the forcer and platen (especially for ironless motors)
Cables:
Allow for flex in dynamic applications (use drag chains)
Avoid tight bends or stress points
Secure connectors with vibration-resistant locks
Thermal Considerations:
Provide adequate heat sinking or active cooling if duty cycle is high
Monitor surface temperature during operation
Tuning the Motion System
Once the motor, drive, and encoder are physically installed and electrically connected, the system must be tuned.
Servo Tuning Steps:
Motor Identification: Load motor parameters into the drive (can be automatic or manual)
Feedback Configuration: Ensure encoder signal is correctly interpreted
Loop Gain Adjustment: Start with current loop, then velocity, then position
Filter Application: Add notch filters or low-pass filters to suppress resonance
Tools:
Use the drive's tuning software (Delta ASDA, Kollmorgen Workbench, etc.)
Run motion profiles to evaluate overshoot, settling time, and vibration
Testing and Validation
Before full deployment, run system validation checks:
Perform test cycles at various speeds and loads
Use oscilloscopes or data loggers to analyze position/velocity feedback
Monitor temperature and current draw over time
Key Performance Metrics:
Positional accuracy
Repeatability
Overshoot and settling time
System stability under load
Common Integration Challenges & Fixes
| Problem | Possible Cause | Suggested Fix |
|---|---|---|
| No motion | Miswired phases or feedback | Verify wiring and encoder polarity |
| Jitter or unstable movement | Gain too high / encoder noise | Reduce loop gain, check grounding |
| Overheating motor | Continuous load exceeds rating | Improve cooling, adjust duty cycle |
| Feedback loss | Loose cable or EMI interference | Secure connectors, use shielded cables |
Smartwin Support for Integration
we provide:
Motor datasheets with detailed electrical and mechanical specs
Encoder installation and alignment guidelines
CAD models for mounting design
Recommended drive pairings
Remote support for tuning and configuration
Pro Tip: When in doubt, request Smartwin's servo integration service to accelerate time-to-market and reduce setup errors.
Conclusion
Integrating linear motors with servo drives and encoders is the key to unlocking the full performance of a modern motion system. With proper component matching, careful mechanical design, and methodical tuning, Smartwin's linear motors can deliver industry-leading speed, precision, and reliability.
Whether you're building a high-speed pick-and-place robot or a micron-accurate metrology stage, Smartwin's engineering team is here to help you integrate with confidence.
Contact us at zhiyingmotor.com to start your integration journey today.















 En
En