Introduction
Manufacturing is entering a new era, often called Industry 4.0—a digital revolution where machines, people, and systems work together seamlessly. This transformation relies on smart sensors, real-time data, and advanced automation. At the heart of this innovation lies an unsung hero: the encoder.
Encoders, whether optical, magnetic, or hybrid, provide the positional and speed feedback necessary for precision, control, and adaptability in modern production environments. Without them, advanced technologies like robotics, CNC machining, automated warehouses, and laser cutting systems would lack the accuracy that Industry 4.0 demands.
This article explores the role of encoders in Industry 4.0, their applications, benefits, challenges, and what the future holds for smart manufacturing powered by encoder technology.
What Are Encoders and Why Do They Matter in Industry 4.0?
An encoder is a motion feedback device that translates rotational or linear movement into electrical signals. These signals are then interpreted by controllers, PLCs, or CNC systems to determine position, velocity, and direction.
In traditional manufacturing, encoders simply ensured machine precision. But in Industry 4.0, they've evolved into intelligent sensors that:
Provide real-time data for connected systems.
Enable predictive maintenance by signaling anomalies.
Support adaptive control, where machines adjust themselves automatically.
Integrate seamlessly with IoT platforms, robotics, and digital twins.
Without encoders, the vision of smart factories—where every component is tracked, optimized, and automated—would remain incomplete.
Types of Encoders in Smart Manufacturing
Optical Encoders
Use light beams and gratings to measure position.
Provide extremely high resolution, essential for CNC machining, semiconductor production, and laser processing.
Common in environments where micron-level accuracy is required.
Magnetic Encoders
Use magnetic fields to detect motion.
More durable than optical encoders—work well in dusty, oily, or harsh industrial environments.
Widely used in woodworking, packaging, and heavy machinery.
Absolute Encoders
Provide a unique digital position value at every point.
Ideal for robots, autonomous systems, and multi-axis machines, where exact position must always be known—even after power loss.
Incremental Encoders
Output pulses as the shaft rotates or slides.
Common for speed monitoring, conveyor systems, and motor feedback.
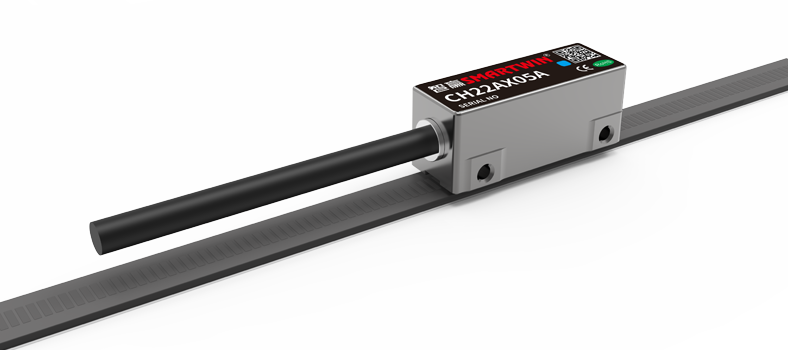
Hybrid & Smart Encoders
Newer encoders like Smartwin combine optical and magnetic technologies.
Equipped with LED indicators, large assembly gap tolerance, and IoT-ready interfaces.
Represent the next generation of encoders for Industry 4.0.
The Role of Encoders in Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is about data-driven efficiency,and encoders are vital to this shift. Here's how they fit in:
Real-Time Motion Feedback
Encoders give machines precise positional and velocity data, ensuring accuracy in CNC tools, robotic arms, and laser cutters.
Predictive Maintenance
By monitoring deviations in signals, encoders can predict wear or misalignment. Maintenance teams can fix issues before failures occur, reducing downtime.
Digital Twins
Encoders feed data into digital twins—virtual replicas of machines. This allows simulation of performance and detection of inefficiencies without halting production.
Seamless Robotics Integration
Robots rely on encoders for:
Linear motion in robotic arms
Rotary motion feedback for joints
Navigation in autonomous robots (AMRs/AGVs)
Mass Customization
Industry 4.0 emphasizes flexible production lines. Encoders allow machines to adapt on the fly to new product designs without sacrificing accuracy.
Key Applications of Encoders in Smart Manufacturing
CNC Machining and Machine Tools
Encoders enable:
Ultra-precise milling and turning
Multi-axis coordination
Automated tool positioning
Laser Processing
Encoders ensure:
Stable beam alignment
Micron-level accuracy in cutting/engraving
Consistent performance at high speeds
Robotics and Cobots
Encoders power:
Robot arm linear motion
Safe human-robot collaboration through feedback systems
High-resolution motion control for delicate assembly tasks
Packaging and Logistics
Encoders are vital in:
Conveyor systems
Pick-and-place automation
Warehouse robotics (AGVs, sorting machines)
Woodworking and Heavy Industry
Magnetic encoders thrive in dusty, high-vibration conditions.
Enable precision cutting, sanding, and shaping.
Benefits of Encoders in Industry 4.0
High Precision – Support micron-level tolerances.
Flexibility – Easily adapted to multiple applications.
Durability – Especially in hybrid or magnetic designs.
Connectivity – IoT-ready encoders allow data sharing and remote monitoring.
Efficiency – Reduce waste, downtime, and energy usage.
Scalability – Suitable for small workshops to mega smart factories.
Challenges and Considerations
While encoders are essential, manufacturers face challenges:
Compatibility – Integrating encoders with legacy PLCs can be tricky.
Cost – High-resolution encoders may increase project costs.
Training – Technicians must understand optical vs magnetic encoder behavior.
Data Overload – Smart encoders generate massive data—processing it effectively requires strong IT infrastructure.
The Future of Encoders in Industry 4.0
Encoders will evolve to support:
AI-Driven Analytics – Encoders will feed machine learning models to predict and optimize processes.
Smaller, Smarter Designs – Compact encoders with multi-resolution modes.
Wireless Connectivity – Reduced cabling, increased flexibility.
Integration with Edge Computing – Real-time processing directly at the machine.
Sustainability – Encoders will help optimize energy use and minimize waste.
Encoders like Smartwin's hybrid optical-magnetic model exemplify the direction—robust, compact, high-resolution, and Industry 4.0 ready.
Conclusion
Encoders are no longer just feedback devices. In the era of Industry 4.0, they have become intelligent motion sensors, enabling real-time data, predictive maintenance, robotics integration, and mass customization. From CNC machining and laser processing to robotics and woodworking, encoders are central to the smart factory revolution. As manufacturers push toward greater efficiency, sustainability, and automation, encoders like Smartwin will continue to play a defining role. The future of smart manufacturing is precise, connected, and data-driven—and encoders are the key to making it possible.















 En
En


